Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a highly contagious and life-threatening disease. It is present throughout the world, although with a higher prevalence in Asia and Africa.
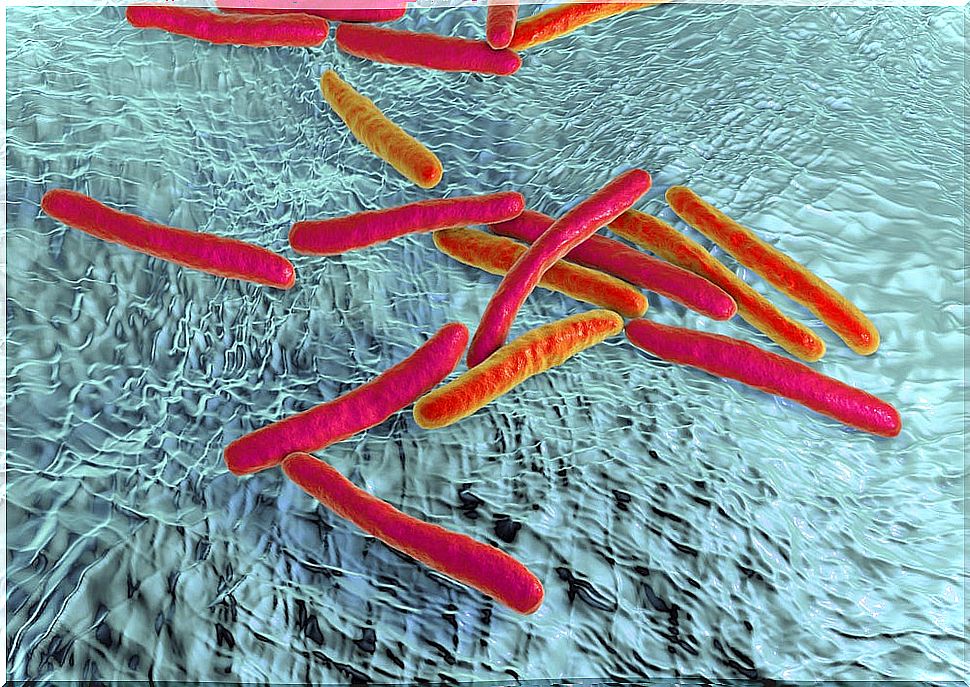
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis . In ancient times it was known as “consumption” and it is estimated that it has existed for more than 20,000 years.
According to the World Health Organization, more than a third of humanity has been exposed to the bacteria. It is estimated that currently 30% of the inhabitants of the planet have the disease in a latent state. Of that percentage, at least 10% will develop active tuberculosis.
Each year about 8 million people become ill with tuberculosis. Within that group, about 2 million die from the disease. Africa and Asia are the regions of the world with the highest incidence of tuberculosis in the world.
Causes and characteristics of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a highly contagious disease. It usually attacks the lungs , but it can also spread to other parts of the body. If not treated properly, this infection could lead to death. Between 10% and 20% of patients die.
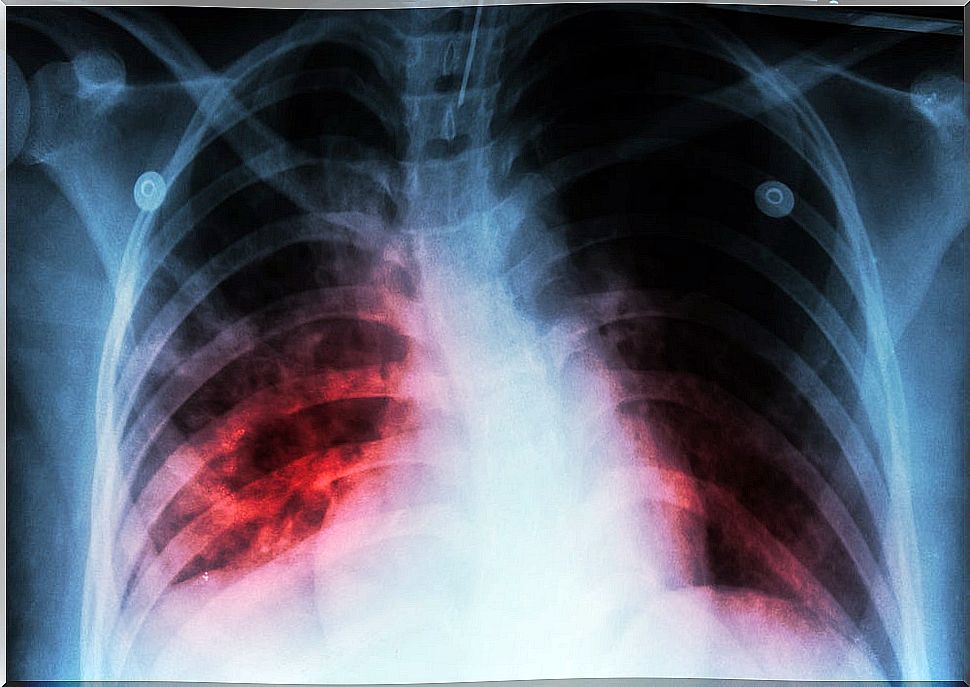
The bacteria responsible for tuberculosis are spread through the air and spread from one person to another. Such microorganisms are released when someone who is sick coughs, sneezes, sings, or talks. Those nearby can absorb the pathogen.
There are two modes of disease: latent tuberculosis infection and tuberculosis disease. In the latent mode, the bacteria are inside the body, but they do not manifest. In that case there are no symptoms, nor can it be spread to others. If the bacterium is activated, its manifestations become evident and the disease takes its course.
In a few cases, the spread of tuberculosis occurs through food. In particular, unpasteurized milk has the risk of transmitting the bacteria. This is not frequent, but it does have a certain recurrence in countries with limited resources.
Types of tuberculosis
There are basically two types of tuberculosis:
- Pulmonary : it mainly affects the lungs and is called “primary infection”. It usually appears immediately after infection.
- Extrapulmonary.
If the symptoms appear up to two years after being infected, it is called “adult tuberculosis” or “post-primary disease”. In this case, the infection is more aggressive and spreads more easily throughout the rest of the body.
The most common forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis are:
- Genitourinary.
- Tuberculous peritonitis.
- Tuberculous meningitis.
- Tuberculous pericarditis.
- Miliary, or disseminated through the bloodstream.
- Tuberculous lymphadenitis, bone and joint, gastrointestinal, liver and, rarely, on the skin.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main symptoms of the disease are intense cough, lasting more than three weeks, in which there is presence of blood or sputum ; chest pain also occurs. Some additional symptoms may appear such as:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Lack of appetite.
- Fever and chills
- Weight loss.
- Sweating during the night
The means used to make the diagnosis is the “tuberculin test”, also called the “Mantoux test”. This consists of administering a substance intradermally and observing the local reaction after 72 hours. In pregnant women, the diagnosis is corroborated with a chest X-ray.
When the diagnosis is positive, the patient must start a treatment that is only effective if he follows it to the letter. Health personnel will ask those close to the patient to also undergo a tuberculin test, since there is a probability that they have the disease, either latently or actively.
Risk factors and prevention
The main risk factor is exposure to an infected person, or to an area where the disease has manifested itself. There is a greater chance of developing the disease as such, when one or more of the following criteria are met:
- Being a child under 5 years old.
- Being infected with HIV.
- Having health problems that affect the immune system.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol, or using drugs.
- Having previously suffered from tuberculosis or having the bacteria in a latent state.
There is a vaccine against tuberculosis, but its effectiveness is relative. Therefore, the best way to prevent the disease is by taking maximum precautions against contagion. Likewise, consult the doctor as soon as possible, in case of suspicion. Early detection of the disease is essential for proper treatment and to avoid contagion.
In conclusion, although the incidence of tuberculosis is very low in the West, we recommend you see your doctor if you develop symptoms similar to those described in this article. A quick diagnosis and early treatment will significantly improve the prognosis of the disease.