Diseases Of The Newborn Treated With Surgery
Most neonatal surgical diseases are related to malformations in prenatal development. There are countless reasons that require surgical intervention for the newborn. Below we will explain only some of them, ordering them by systems.
Digestive surgical diseases
Anterior abdominal wall defects
In this regard we find omphalocele and gastroschisis. The omphalocele is that abdominal some organs protrude through an opening in the abdominal wall. In addition, these organs are covered by a membrane. In gastroschisis there is no such membrane.
Esophageal atresia

In the context of esophageal atresia, the esophagus does not develop properly. Thus, it ends up at the top without actually connecting with the stomach.
Esophageal atresia is frequently associated with another defect called a tracheoesophageal fistula. This determines an abnormal connection between the esophagus and the trachea. In this way, the digestive content ends up passing to the respiratory system.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
The pylorus is the hole that connects the stomach with the intestine. In the course of this disease, the muscles around the pylorus become hypertrophied (their size is increased). Because of this, the passage of food from the stomach to the intestine becomes difficult.
Pyloric stenosis has consequences such as frequent vomiting, malnutrition, or abdominal pain.
Megacolon: Hirschprung’s disease
Peristalsis is a term that refers to the contractions that the intestine makes in order to mobilize food. For these movements to occur, the presence of neurons in the intestinal wall is necessary. This is precisely what is lacking in Hirschprung’s disease, at least in part of the intestine.
As a consequence of not producing peristalsis in an area, a blockage is generated in it. Food cannot move forward and after the blockage, it accumulates. This generates a significant intestinal obstruction. The abdomen swells and bowel movements become difficult.
Cardiovascular surgical diseases
Congenital heart disease is the main congenital malformation that causes infant and neonatal mortality. This is explained by its relative higher frequency and its higher specific mortality.
Coarctation of aorta
The aorta is the artery that carries blood from the heart to most of the blood vessels in the body. A coarctation of the aorta refers to a specific narrowing of this artery, usually at the beginning of its course.
Symptoms depend on the amount of blood that can flow through the coarctation. If it can flow enough, it won’t be diagnosed until around adolescence.
Otherwise, the newborn will present rapid breathing and eating problems. You will also be sleepy and overreact to stimuli. If the coarctation is very severe, the newborn may present with heart failure and shock.
Atrial and ventricular septal defect
The heart has two atria (right and left) and two ventricles of equal distribution. The cardiovascular circuit determines that there is oxygenated blood in the left cavities and non-oxygenated blood in the right.
When there is communication between the right and left atrium (or ventricle), these two bloods are mixed. This means that oxygen cannot reach all cells correctly. In this way, the neonate will present symptoms such as respiratory distress and shortness of breath with activity, for example when eating.
Pulmonary stenosis
There are valves that pass blood from the heart to the arteries. It may be the case that these valves cannot be fully opened. This is called a valve stenosis. In this case, it happens with the valve that leads to the pulmonary artery: the one that carries non-oxygenated blood to the lungs to be oxygenated.
Most cases of pulmonary stenosis are mild and are found on auscultation of the newborn.
Urological surgical diseases
Migration and fusion anomalies
In prenatal development, the kidneys form in the lower abdomen. Later, they ascend until they finish at the top. Faults may occur along the way, leading to renal ectopias. This term refers to kidneys located in abnormal places.
Also, the kidneys, while ascending, can meet. Thus, it is possible that they fuse, giving rise to a single kidney. When they are joined at the bottom, they give rise to the so-called horseshoe kidney, due to the shape it acquires.
Multicystic renal dysplasia
A kidney with multicystic renal dysplasia is composed of cysts and dysplastic (abnormally maturing) tissue. Thus, the kidney does not work, and usually ends up regressing. The ureter (the tube that connects the kidney to the bladder) often appears to be stressed or fails to develop.
Surgical diseases of the nervous system
Hydrocephalus
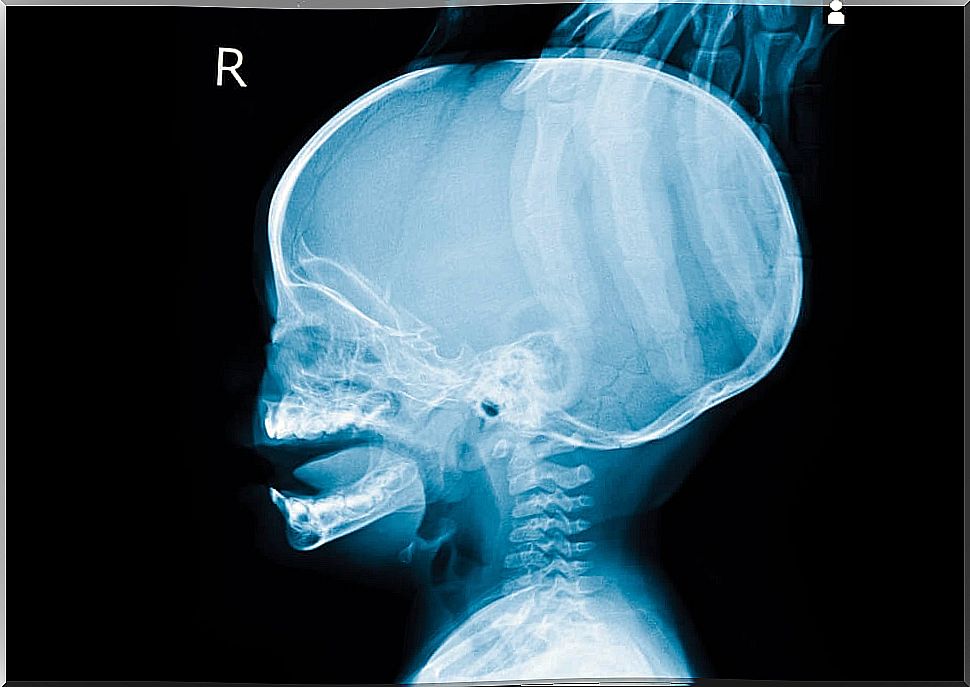
Hydrocephalus is the accumulation of fluid in the deep cavities of the central nervous system. This fluid compresses the brain. With the naked eye, it can be seen by the increased size of the neonate’s head.
It can produce a variety of symptoms, from vomiting to drowsiness and irritability or seizures.
Spina bifida
When the spinal column does not close completely, part of the spinal cord protrudes through the back. If too little nerve tissue protrudes, there may be no symptoms. If it is a large amount, there may be motor difficulties or urinary symptoms, among others.