Nutrition And Gallstones, What Should You Take Into Account?
Gallstones, also called cholestasis, is one of the most frequent pathologies of the digestive system. It is defined as the presence of stones in the gallbladder or ducts, which can cause obstructive problems. The size of gallstones can range from the size of a grain of sand to that of a golf ball.
Most cases of gallstones occur asymptomatically, that is, without obvious symptoms that alert the problem. And in symptomatic cases, biliary colic is the main symptom, although an episode of acute cholecystitis may appear directly.
Acute cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is the main complication of gallstones. It is characterized by causing inflammation of the gallbladder along with other discomforts such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and restlessness. There are two types of stones associated with this pathology:
- Cholesterol lithiasis: represents 75% of the cases of gallstones in the West. Its formation takes place by alterations in the metabolism of bile acids and cholesterol.
- Pigmentary lithiasis: it is produced by abnormalities in the metabolism of bilirubin (pigment present in bile). It accounts for 25% of the prevalence of gallstones.
What can cause gallstones?
Although it is not yet clear why gallstones form, there are a number of factors that contribute to the formation of gallstones. It is a pathology that occurs in both sexes, although with a higher prevalence in women.
In cholesterol lithiasis, the main causes of stone formation are:
- Genetic predisposition of the individual.
- Alterations in lipid metabolism.
- Obesity or significant weight changes.
- Alterations in the correct emptying of the gallbladder.
- Infections
- Hepatic cirrhosis.
- Low-fiber, high-fat diet.
- Contraceptive treatment or estrogen therapy.
On the other hand, in pigmentary lithiasis the formation mechanism is complex, since it occurs due to an increase in the bilirubin content in the bile. This is evidenced by a study published in 2020.
General recommendations for gallstones
The general recommendations for people with gallstones should be the following:
- Carry out a varied, balanced diet adapted to individual needs.
- Maintain a healthy weight, avoiding excess weight.
- Eat slowly and chew properly.
- Avoid fasting and large meals, since both promote gallstones.
- Divide the diet into 5 meals a day.
- Perform moderate exercise for more than 40 minutes a day, at least 3 times a week.
- Drink about 2 liters of water daily.
- The culinary techniques that we will use will be: cooking, boiling and papillote.
A healthy diet high in vegetables has been shown to be associated with a lower incidence of these pathologies.
Dietary treatment for gallstones
In people with gallstones, proper nutrition plays a fundamental role, since it facilitates the recovery process, favoring the rest of the gallbladder and facilitating digestive functions. It also helps prevent complications associated with this disease.
In particular, the gallstone diet can help prevent the acute symptoms of biliary colic and alleviate digestive discomfort such as gas and dyspepsia. In case of inflammation (cholecystitis) fasting is advisable, as long as the doctor indicates it.
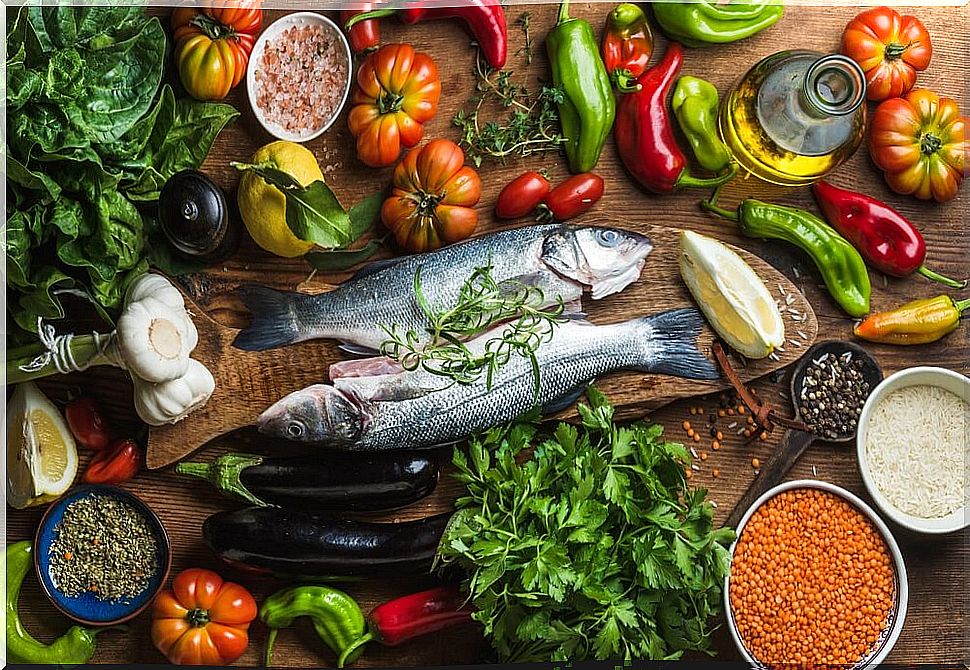

Recommended foods
- Skimmed dairy: milk, yogurt, fresh cheese, kefir, curd.
- Lean meats: lean parts of pork, turkey, chicken (without skin).
- White fish : rooster, sea bass, sea bream, cod hake.
- Egg : in the form of an omelette, scrambled, grilled, poached or cooked.
- Vegetables and vegetables: green leafy (chard, spinach, green beans, artichokes), red and green peppers, zucchini, asparagus. The best tolerance is cooked or pureed.
- Cereals and potatoes : rice, wheat, corn, barley, oats, potatoes.
- Legumes: double cooked, according to tolerance (chickpeas, peas, lentils, beans). Do not accompany with products such as blood sausage, chorizo or bacon.
- Fruits: of all kinds; fresh, in compote, roasted.
- Fats and oils: there is a better tolerance to vegetable fats, such as extra virgin olive oil (preferably raw).
- Drink: water, defatted broths and digestive infusions (chamomile, linden, among others).
There is evidence that the fatty acids of the omega 3 series contribute to exert a protective role at the renal level, especially in those pathologies that have an inflammatory type process.
Limited food
- Fatty foods: oils, butters, margarines, lard, tallow, cream, sauces and fried foods.
- Fatty meats and sausages : blood sausage, chorizo, bacon, veal and lamb.
- Blue fish and shellfish: tuna, salmon, mussels, prawns, prawns, among others. Avoid canned in oil and pickled.
- Other products: pastry, confectionery, spicy foods and pastries.
- Drinks: coffee, tea, soft drinks and alcoholic beverages, acidic fruit juices, drinks with coffee, tea or guarana extracts.
Take care of your diet to avoid gallstones
Are you suffering from gallstones? Then keep these recommendations in mind to support your treatment through diet. Of course, do not stop following the recommendations and treatments suggested by the doctor.