Lumbar Puncture Headaches
The number of patients who experience headaches after a lumbar puncture has been greatly reduced. At the beginning of the 20th century the percentage was 60%. Today it has reached 11%, when the puncture is done with a fine needle.

According to the scientific literature, it is estimated that lumbar puncture headaches affect 40% of patients who undergo spinal puncture or spinal anesthesia. However, there is no need to worry. In general, the discomfort resolves spontaneously.
Lumbar puncture is a procedure performed to apply local anesthesia or for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. On some occasions it causes a reduction in intracranial pressure and this in turn leads to headache.
The first lumbar punctures were performed at the end of the 19th century. At the beginning of the 20th century, the incidence of headache from this procedure was 60%. Over time this percentage has been decreasing and continues to do so.
What is a lumbar puncture?
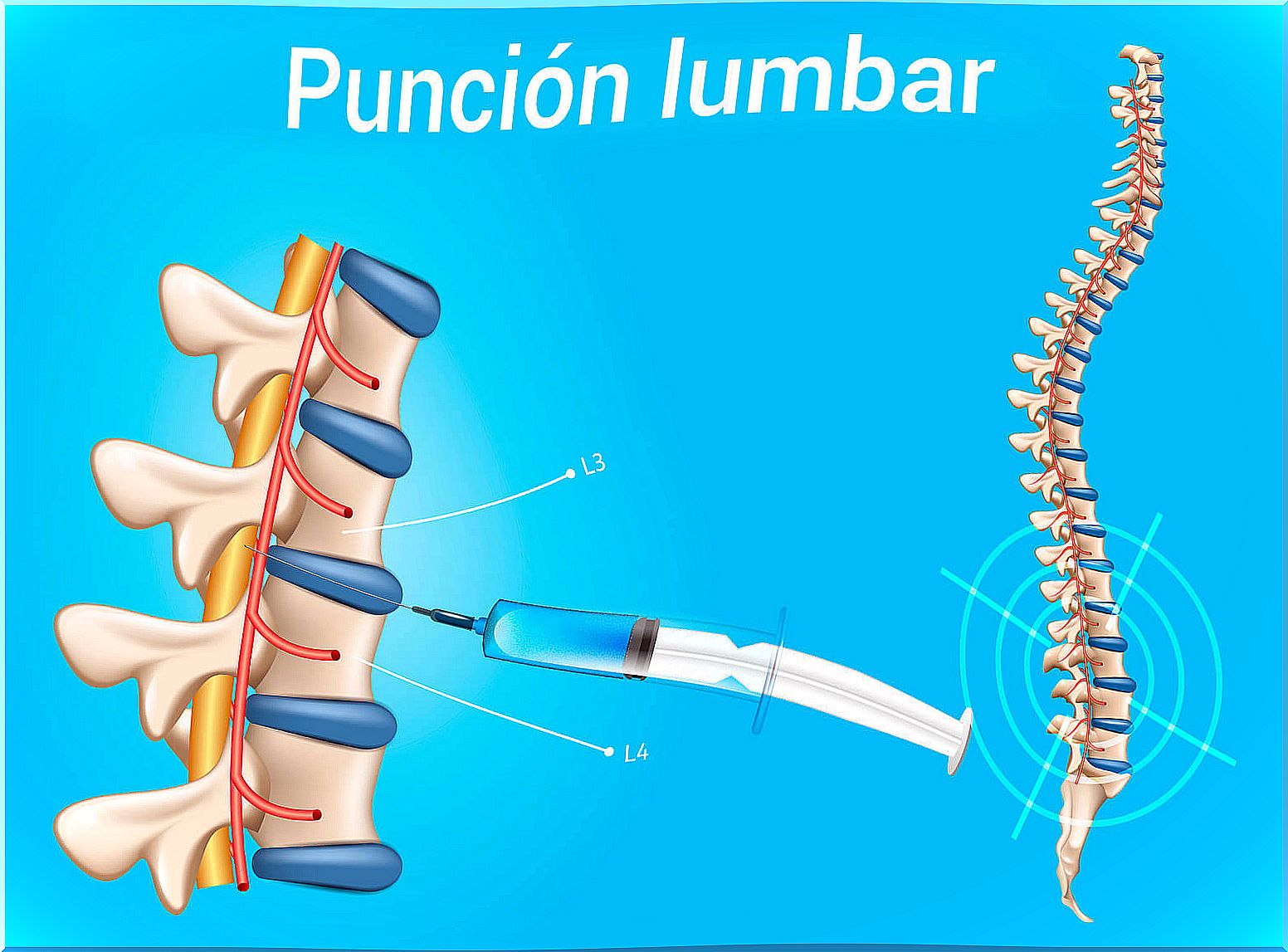
Lumbar puncture is a clinical procedure whose purpose is to extract cerebrospinal fluid . It is also done to apply anesthesia or some medicine. This fluid is found around the brain and spinal cord, and acts as a kind of cushion.
During the procedure, the doctor inserts a needle between two lumbar vertebrae and into the spinal canal. Depending on the purpose of the lumbar puncture, one of the following actions is carried out immediately:
- A small amount of cerebrospinal fluid is removed, which will then be examined in the laboratory.
- A certain amount of fluid is removed to reduce the pressure in the spinal canal.
- Anesthetic or some medicine is injected.
Then the needle is removed. However, if there is a very large loss of cerebrospinal fluid, the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid is reduced in the cranial cavity and this causes a headache.
Headache and lumbar puncture
Headache after lumbar puncture usually presents as bilateral, that is, on both sides of the head. It is usual for it to appear immediately and, in any case, within a period of no more than five days after the procedure. The normal thing is that it disappears spontaneously in less than a week.

In typical cases, the pain worsens when the patient is sitting or standing. Therefore, it is recommended that you remain lying down. Headache occurs mainly in women, between 18 and 30 years of age.
On the other hand, the appearance of headache after lumbar puncture depends largely on the type of needle used, the technique applied and the skill of the operator who performs the procedure. The thinner the needle, the less risk of headache. With very thin needles, the percentage of affected is reduced to 11%.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main symptom of post-puncture headache is a throbbing, dull pain that ranges in intensity from mild to disabling. The pain worsens when the patient stands up and decreases when lying down.
The headache can be accompanied by other symptoms such as dizziness, ringing, blurred or double vision, nausea, hearing loss, and stiffness and pain in the neck. Magnetic resonance images reveal a decrease in intracranial structures, among other signs.
The diagnosis is clinical. Sometimes the doctor will order an MRI or other similar tests to rule out other possible causes of the headache.
Other data to take into account
It is best to lie down for no less than 12 hours if you have a headache after a lumbar puncture. The pain usually appears 15 minutes after sitting up, so it is not contraindicated to perform some actions, such as getting up to go to the bathroom or to eat.

Drinking plenty of fluids helps regain lost cerebrospinal fluid, especially during the 24 hours after the procedure. Likewise, unless otherwise indicated, it is advisable to drink coffee or beverages that contain caffeine.
The headache should go away. If the intensity is maintained or increased several hours after the procedure, it is necessary to consult with the doctor as soon as possible. Also if there is vomiting and tingling or numbness in the legs, difficulty urinating, or pain or bleeding occurs at the site where the needle was inserted.