Spinal Tumors: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Spinal tumors are not easy to detect, as they cause few symptoms at first. Back pain should not be overlooked, especially if it is regular and occurs even at rest.
Spinal tumors are abnormal formations that affect the spine. Sometimes they compromise the bone and its adjacent structures; in this case, they are called a “vertebral or vertebral tumor.”
Vertebral tumors are also considered those that involve the vertebral canal and that affect the nervous structures; in this case it is known as a «myelo-radicular tumor». The tumor can be benign or malignant, but in both cases it can be life threatening.
Most commonly, vertebral tumors form as a result of metastasis; that is, of a malignant tumor that occurs in another area of the body and that spreads to other parts. Usually they come from the prostate, breast, lung or kidney.
Types of vertebral tumors
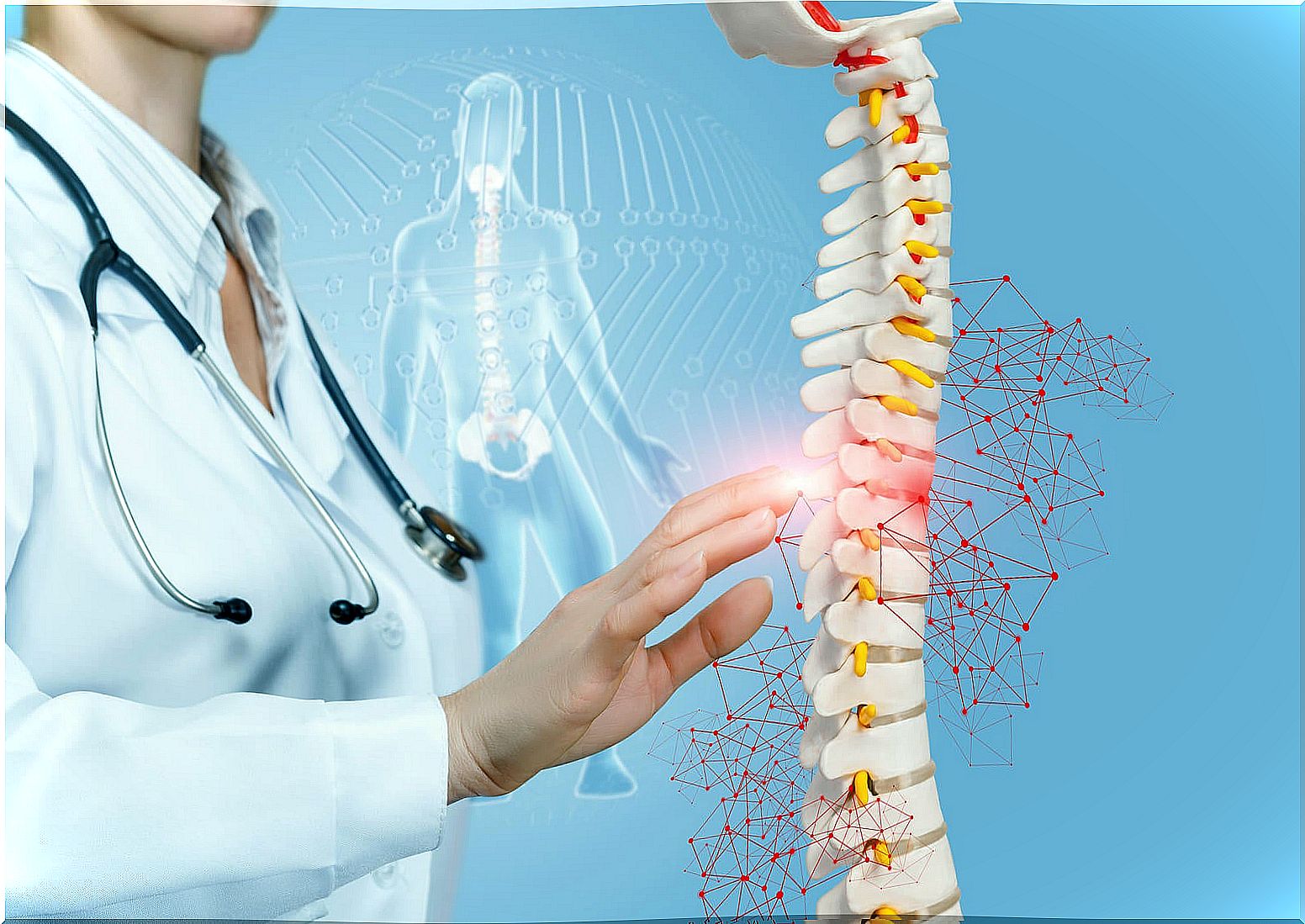
Spinal tumors can be classified in different ways. First of all, they are divided into benign and malignant, depending on their nature. They can also be primary or secondary ; the former arise independently and the latter are the result of metastasis from other tumors.
One of the primary vertebral tumors is plasmacytoma ; This begins in the white blood cells that produce antibodies and can develop into multiple myeloma. Other tumors that may be primary include osteoblastomas, hemangiomas, and osteoid osteomas.
The most common is to classify vertebral tumors by their location. They can be in the spinal column or in the spine, which surrounds the spinal cord. These types of tumors are also known as extradural tumors, as they form outside the marrow.
Causes of a vertebral tumor
Science is not clear about the reasons why primary vertebral tumors form. It is believed that they are the result of abnormal genes, but there is not enough evidence for this yet and it is not known whether they are inherited or the genetic change occurs throughout life.
There are suspicions that there are also some environmental conditions that can give rise to a primary tumor. Continuous and long-term exposure to some chemicals may also play a role.
As we have already noted, the most common is that these tumors are metastatic, that is, the result of the spread of a tumor located in another part of the body. It is important to note that tumors of the breast, prostate and lungs are the ones that most frequently give rise to vertebral tumors.
Symptoms of a spinal tumor
The most frequent and obvious symptom of this type of tumor is pain. Almost always the affected person consults with the doctor for discomfort in the back. Typically, the pain is experienced both at rest and during activity and is not worse when carrying something heavy.
The pain occurs because the tumor grows and compresses the surrounding tissues. There may also be destruction of the vertebra or compression in the spinal cord or nerve roots. Many times people wake up at night because of pain.
It is important to see your doctor if you experience these symptoms. As already noted, even a benign tumor can pose significant health and life risks. Therefore, a pain with these characteristics should not be overlooked.
How is it diagnosed?
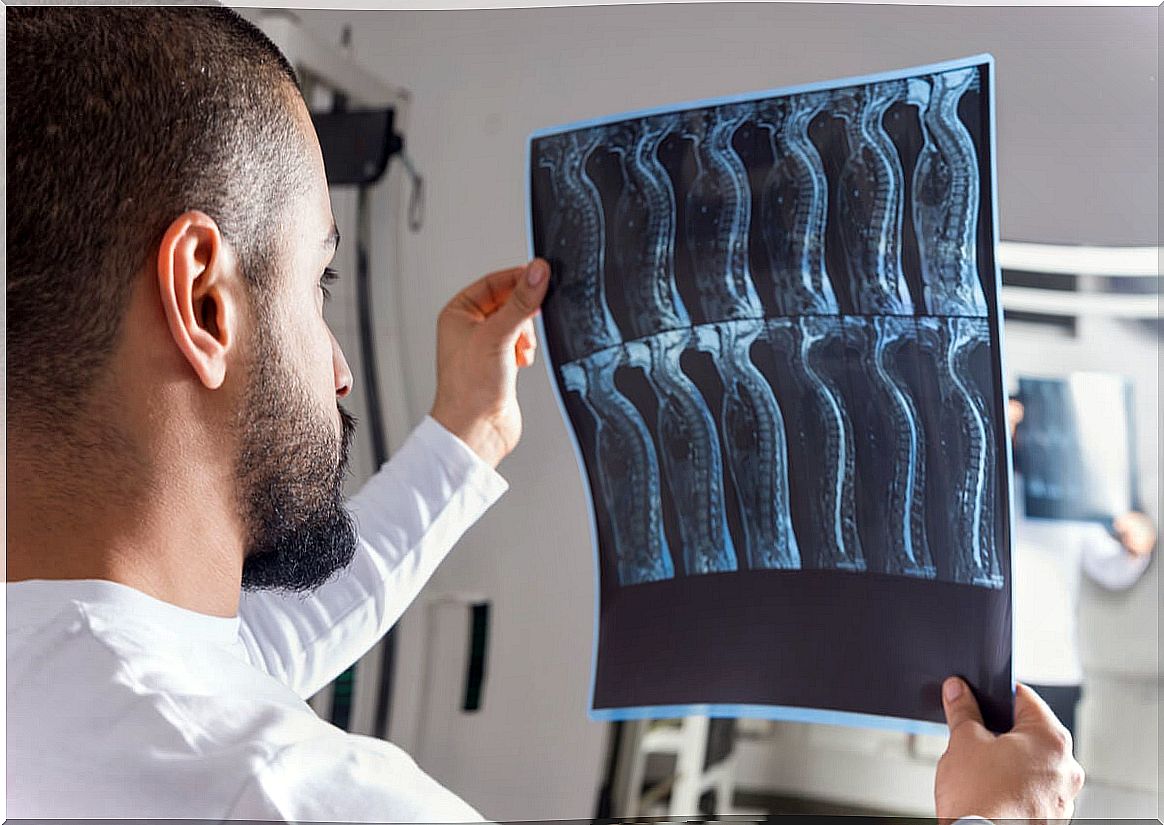
To diagnose a spinal tumor it is necessary to do several examinations and tests. The medical history and symptoms can shed some light, but the diagnosis can only be established from images and laboratory tests.
Typically, the suspicion of a tumor leads to the practice of one or more of the following tests:
- Magnetic Resonance (MRI). It is the preferred test for the diagnosis of these tumors. Typically, a contrast substance is applied. Sometimes a mild sedative is required to reduce the impact of claustrophobia in some people.
- Computed tomography (CT). The most common is that it is combined with Magnetic Resonance. Contrast is also usually applied.
- Biopsy. This type of test is reserved to determine the type of tumor that is present. A sample of tissue is taken and examined in the laboratory. It is usually done by a fine needle radiologist.
Treatment options
The purpose of treatment is to remove the tumor completely. The difficulty is that any mistake or complication can lead to damage to the spinal cord or nearby nerves. The risk is considerable and, therefore, the situation must be carefully evaluated before deciding what treatment to follow.
The treatments available for spinal tumor are as follows:
- Supervision and monitoring. If the tumor is small, benign and does not involve nearby tissues, it is indicated to monitor it periodically. This will be done through diagnostic imaging.
- Surgical intervention. Surgery is a valid option when the risk does not exceed the limits of what is reasonable. Sometimes the tumor cannot be completely removed and postoperative procedures are needed. Recovery can be tough.
- Radiation therapy. It is used to treat tumors that are too risky for surgery and those that are inoperable. Also as a complement to an incomplete excision. It is sometimes used to reduce pain. It creates risks for the surrounding tissues and can cause annoying side effects.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery. It is not a surgery as such, but the application of a high dose of radiation in a very specific area. It is a very effective technique, but inapplicable in certain cases. It also involves risks, such as vertebral fracture.
- Chemotherapy. It can be an advisable treatment for some malignant tumors. It may be combined with other techniques. It usually causes side effects such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss and an increased risk of infections.
- Other drugs. Some of the treatments can cause inflammation of the spinal cord. If this happens, corticosteroids are usually prescribed to treat the problem. It is only done for a short time due to the side effects of these types of medications.
Visiting the doctor in the face of ongoing pain
Spinal tumors are a serious health problem. These types of formations can cause compression or damage. This may result in reduced mobility or tenderness in the area below the tumor.
Sometimes they cause dysfunctions in the intestine or bladder. They could also damage the spine and create instability, thus increasing the risk of fracture or collapse of the spine. Both conditions could affect the spinal cord.
If these tumors are found early, they are much easier to treat and pose fewer risks. The probability of recovery is also increased. Some vertebral tumors, by themselves, are life-threatening.