What Role Do Carbohydrates Play In The Diet
Carbohydrates are essential for humans. They are the source of energy for the brain and other nervous tissues. They are stored in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen. Subsequently, they are transformed into glucose and produce energy. Athletes are especially dependent on these nutrients. In the case of sedentary people, things could change.
In this article we explain what types of carbohydrates there are and what their functions are in the body. You will also learn what role these macronutrients play in the diet. In this way you can include them in the diet with full knowledge of the facts. Keep reading!
The carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, especially glucose and glycogen, are the energy source from which the body is supplied. Thanks to them, the body can carry out different activities. They are so important that muscle fatigue is associated with the lack of availability of sugars.
Therefore, an adequate amount of glucose is key to be able to perform a certain physical exercise with the appropriate intensity. This is because the oxidation of proteins and fats produces slower energy than carbohydrates.
Types of carbohydrates
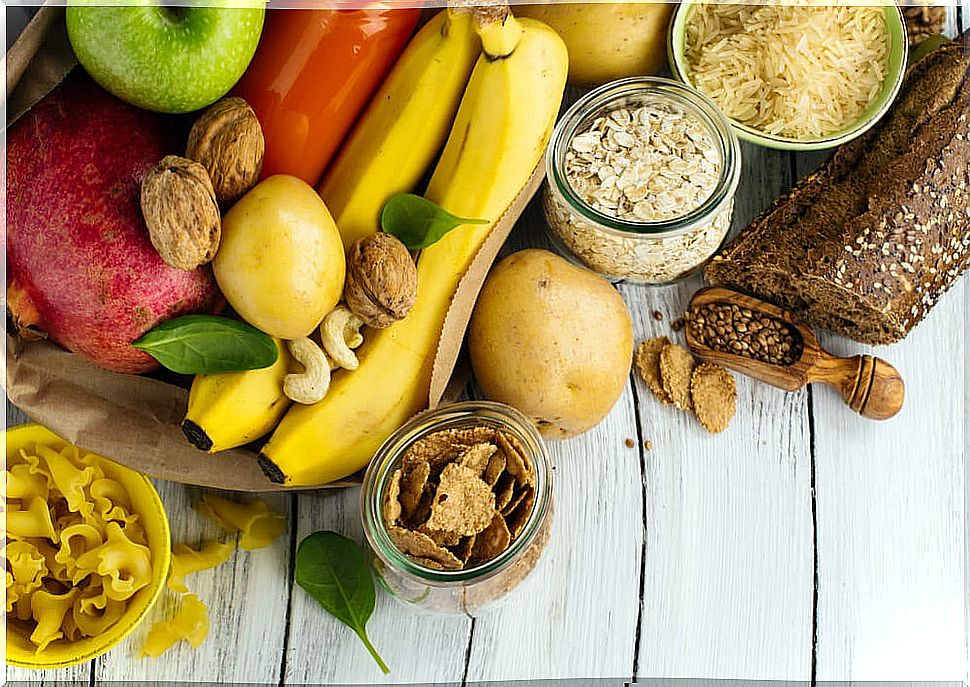

There are different classifications of carbohydrates. Based on the number of glucose molecules, simple and complex carbohydrates can be distinguished:
- Simple carbohydrates: within these are monosaccharides – made up of a glucose unit -, such as glucose, fructose and sucrose; and disaccharides – made up of two glucose units – such as lactose, galactose and maltose. Some simple carbohydrate-rich foods are: sugar, whether white or brown, honey, molasses, and fruit juices. Also, simple carbohydrates may or may not have fibers.
- Complex carbohydrates: also called polysaccharides, they are made up of many glucose units linked together that form very long chains, such as starch or fibers. Some foods rich in complex carbohydrates are wheat, rice, barley, potatoes, chickpeas or green beans.
The quality of carbohydrates is determined by their complexity. In this way, the regular intake of simple or simple sugars is usually counterproductive, except in the case of athletes. There is sufficient scientific evidence to associate frequent consumption of simple carbohydrates with a higher incidence of metabolic diseases.
Carbohydrate functions
The main functions of carbohydrates are as follows:
- Energy supply: carbohydrates function as an energy reserve, and can be used immediately. Energy pantries have the ability to move quickly to produce glucose when needed. This function means that the contribution of carbohydrates has to be daily.
- Protein savings: by using carbohydrates as a source of energy for the body, the use of proteins for this purpose is set aside. In this way, hypertrophy processes are favored.

- Formation of important tissues: carbohydrates are an essential part of connective and nervous tissues. In addition, they are also found in DNA molecules and adenosine triphosphate or ATP, a nucleotide necessary for energy.
- Helps Against Ketone Bodies: When the body does not have enough carbohydrates for energy, it uses fat instead. For this reason, wastes are produced that are known as “ketone bodies”. Formerly it was speculated that these compounds were harmful, so carbohydrates prevented their creation. This theory has now been discarded. Ketone bodies are efficient fuel for the brain.
Carbohydrates as regulators of the body
In addition to participating in all the above tasks, the cellulose or dietary fiber present in carbohydrates is responsible for regulating intestinal transit. This, therefore, has other beneficial health effects, such as:
- Reduction of constipation by softening the stool and increasing its volume.
- Increased feeling of fullness, which allows better control of food intake.
- Slowdown in the emptying of the stomach, which allows better management of ingested food.

- Decreased absorption of substances such as cholesterol.
- In the case of diabetic people, it reduces the rise in blood sugar , allowing a better control over this factor.
- Protective effects against colon cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Fiber consumption is also associated, as stated by research published in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition , with a reduction in the incidence of colon cancer.
Carbohydrate sources
Carbohydrates are present in a wide variety of foods that are regularly consumed. In fact, in any balanced diet, the sources of this nutrient must correspond to 50% of the total calories. Foods that provide it include:
- Cereals: such as rice, wheat, corn, oats and millet, among others.
- Pasta: macaroni, spaghetti, noodles, etc.
- Assorted fruits and vegetables.
- Milk and its derivatives: butter, cheese, etc.
- Tubers and roots.
- Sugar: cane, beet, honey or molasses. Its consumption should be moderate.
- Bread and bakery products.
In any case, those simple sugars present in sweet and ultra-processed foods should be avoided. The consumption of these products is associated with a worse state of health according to experts.
Introduce quality carbohydrates into the diet
The presence of complex carbohydrates in the diet can be beneficial for health. However, it is necessary to avoid the consumption of added and simple sugars. Always try to choose foods rich in fiber and avoid refined flours.